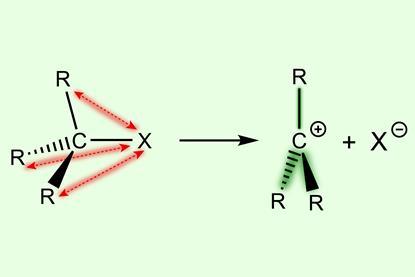
Chemical bonding
In this collection we explore the fundamental principles of chemical bonding, covering covalent, ionic, and metallic bonding, as well as molecular structure, intermolecular forces, and the role of chemical bonding in shaping the properties and behaviour of molecules.
The mechanical side of bonding
Synthetic chemists are finally mastering the assembly of interlocked molecules held together by the mechanical bond, find James Mitchell Crow
Reaching into the non-covalent toolbox
Alongside supramolecular stalwarts, budding bonding forms are vying to be valuable, finds Andy Extance
When a bond gets too extreme
Chemical bonds are part of the way chemists rationalise the behaviour of atoms in the conditions of the world around them. Tim Wogan looks at how they are affected when those conditions change
Towards a unified theory of bonding
Explaining trends across the periodic table with the help of node-induced electron confinement
Bonds are the ties that bind chemistry
Those seemingly simple sticks belie our most complex concept
Do bond classifications help or hinder chemistry?
Ionic, covalent, metallic and more… but there’s debate about whether bonds are real at all
The forgotten female crystallographer who discovered C–H⋯O bonds
Andy Extance tells the overlooked story of crystallographer June Sutor, whose C–H⋯O bonding hypothesis was unjustly suppressed
The bonds that bind
Chemical bonds continue to fascinate chemists – and bring us together too
What is a bond?
There’s more to bonding than covalent, ionic and the lines we draw between atoms on paper. Philip Ball takes on the expanding list of chemical connections
- Research
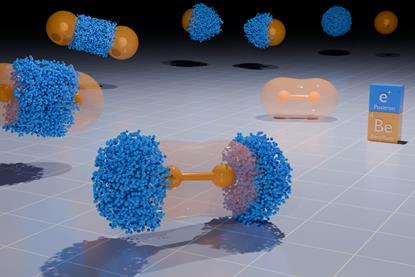
Unexpected stability theorised in positron-bound beryllium dimers
Simulations challenge conventional ideas about positronic interactions
- Research
‘Plumbyne’ compound featuring multiple carbon–lead bonds synthesised
Relatively weak π bonding in the structure opens up possibility for various chemical reactions
- Research
Paramagnetic NMR used to probe covalent character of halogen bonds
Assessing hyperfine shifts in paramagnetic NMR spectra provides new details on the covalent character of halogen bonded cocrystals
- Research
Water squeezed into 2D channels conducts electricity 100,000 times better
Network of quasi-2D hydrogen bonding may be responsible for effect
- Research
Electron irradiation converts hydrocarbon crystals into nanodiamonds
Flawless nanodiamond synthesis that wasn’t thought possible accomplished by transforming adamantane
- Research
Discovery of unusual iodine–silver bond opens up new possibilities for coordination chemistry
Crystallographic studies reveal that the bond is similar in length to typical metal–metal bonds
- Research
Nobelium becomes heaviest element with identified compounds
Complexes containing hydroxide, water and dinitrogen ligands detected as researchers probe chemistry on the edge of the actinide series
- Research
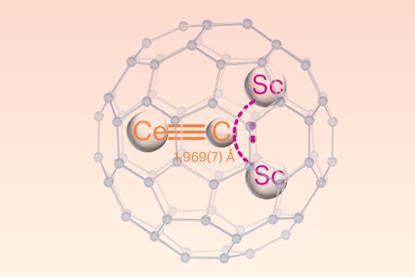
Lanthanide–carbon triple bond synthesised and characterised
Cluster stabilised within a C80 fullerene cage
- Research
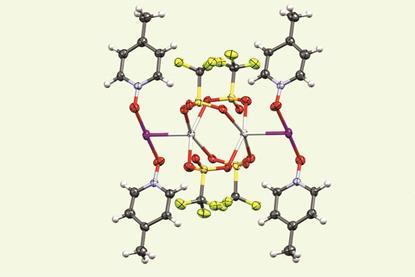
Actinide bonding could be tweaked by adjusting oxidation states
Modelling reveals that control of mysterious phi bonds could change behaviour of f-block elements
- Research
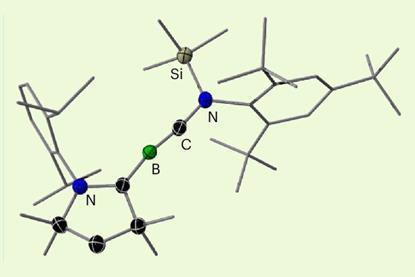
Carbon–boron triple bond formed for the first time in a neutral novel molecule
Synthesis could help chemists better understand bonding
- Research
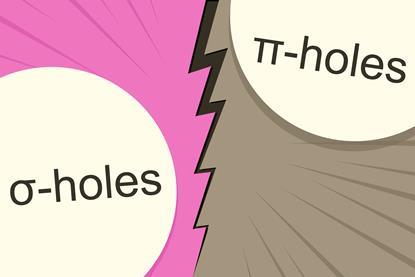
Computational study says nucleophile finds σ-holes more attractive than π-holes
A σ-hole leads to a stronger bond with NH3 than a π-hole on the same atom
- Opinion
A high-pressure insight into the structure of water
The hydrogen-bonded network in liquid water resists compression; density increases instead arise from molecules moving into voids
- News
Beyond hydrogen bonding: new definitions for secondary bonding interactions to end confusion
The 20-year struggle to define secondary bonding interactions
- Webinar
Copper-catalysed carbon-heteroatom bond-forming processes
Explore cutting edge copper-catalysed carbon-heteroatom bond formations used in industrial applications
- News
Robert Mulliken’s Nobel prize medal latest to go up for auction
Mulliken won the Nobel prize in chemistry in 1966 for developing molecular orbital theory
- Feature
Illuminating antiaromaticity
Aromaticity’s dark alter-ego is ready to emerge into the sunlight. James Mitchell Crow talks to the scientists trying to exploit the instability
- Webinar
Lab XAS: a new tool for materials characterisation
Explore the utility of lab XAS as an everyday tool for materials characterisation
- Research
All-metal fullerene cluster made for first time
Dodecahedral structure offers new insight into metal bonding
- Research
Van der Waals crust behind simple parameter that can describe chemical bonds
Penetration index provides a fresh perspective on two-atom interactions
- Research
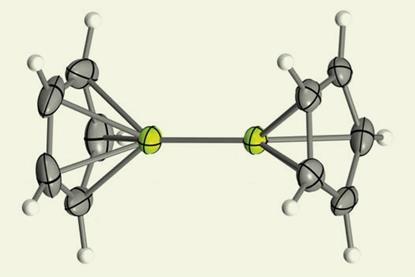
Half-century quest to create stable beryllium–beryllium bond ends in success
Organoberyllium sandwich compound should provide answers to questions first posed a century ago
- Research
‘Dynamic bonds’ reshape the rules of aromaticity and chirality
Discoveries could contribute to new understanding of organic chemistry, triggering applications in catalysis and materials science
- Research
Quantum chemical analysis uncovers previously overlooked contributor to carbocation stability trend
Introducing substituents destabilises the parent substrates
- Research
Benzene’s bond lengths corrected
Sophisticated spectroscopic method shows that previously reported values were out by several milliangstroms